Northern Great Plains Water Resoureces
Discovering Archeological Sites Utilizing NASA Earth Observations to Detect Changes in Snowpack Coverage in Intermountain National Parks
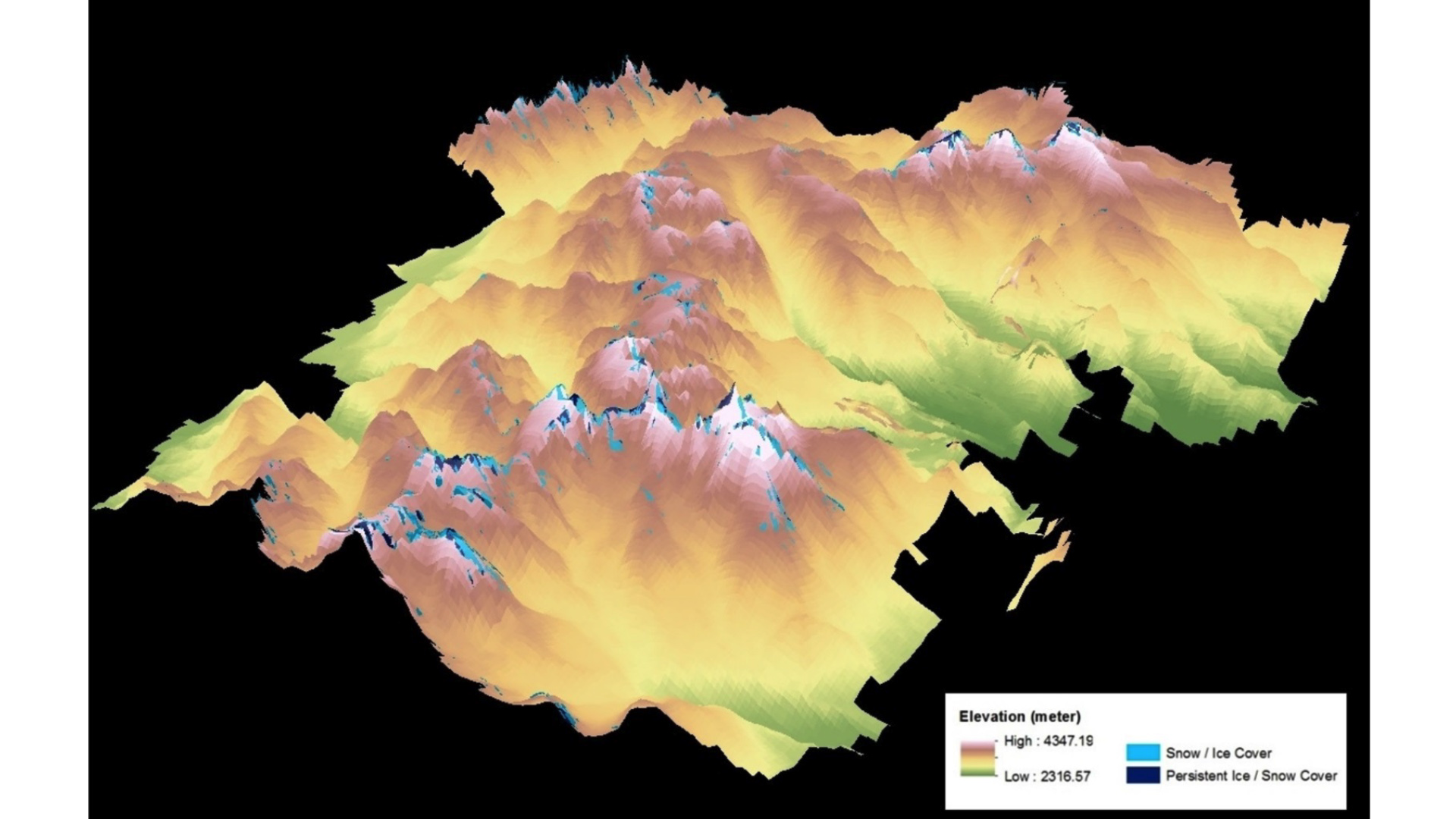
National Parks in the Intermountain region of the northern United States Great Plains are experiencing snow and ice melt due to changes in climate. As the ice recedes, it has the potential to reveal previously undiscovered archaeological sites. Therefore, investigating the changes of Persistent Ice and Snow Cover (PISC) in this region is crucial to identifying archaeological sites. To address the changes of PISC, a two phase methodology was implemented: 1) map the PISC in the Rocky Mountain National Park, CO over the period from 1998 to 2014 using Landsat scenes; and 2) detect the changes of PISC over time. This research was a case study to document the retreat of PISC in the Intermountain National Parks, namely Rocky Mountain National Park, by applying NASA Earth observations. This research can also aid in testing hypotheses about the drivers of human behavioral variability and support the National Park Service in its mission to mitigate impacts of climate change to mountain cultural heritage resources.
- Location
- Wise County Clerk of Court's Office
- Term
- Summer 2016
- Partner(s)
- National Park Service, Intermountain Region
National Park Service, Rocky Mountain National Park (RMNP) - NASA Earth Observations
- Landsat 5, TM
Landsat 8, OLI - Team
- Anne Gale (Project Lead)
Michael Brooke
Xin Hong
Cody Vineyard - Advisor(s)
- Dr. Kenton Ross (NASA DEVELOP National Program)
Dr. DeWayne Cecil (NOAA NCEI, Global Science and Technology)
Bob VanGundy (The University of Virginia's College at Wise)
Mike Bender (NASA DEVELOP National Program)
Project Video